What Would Cause a Cylinder to Lose Compression?: Top Reasons Revealed
A cylinder can lose compression due to worn piston rings or a damaged cylinder head gasket. When a cylinder loses compression, it can result in decreased engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Identifying the root cause of this issue is crucial to prevent further damage to the engine. Regular maintenance checks and prompt repairs can help maintain optimal compression levels in the cylinders. In this blog post, we will explore the common reasons why a cylinder may lose compression and discuss the importance of addressing this issue promptly.
By understanding the causes and symptoms of compression loss, you can take proactive steps to keep your engine running smoothly.
Introduction To Engine Compression
Engine compression loss in a cylinder can be caused by worn piston rings, cracked cylinder walls, or a faulty head gasket. These issues can lead to reduced power, increased fuel consumption, and poor engine performance. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are crucial to prevent compression loss.

When it comes to internal combustion engines, compression plays an essential role in the combustion process. Compression occurs when the piston moves upward, compressing the air and fuel mixture in the cylinder. This compression creates pressure, allowing for the spark plug to ignite the mixture and power the engine.
However, if there is a loss of compression, the engine will not function correctly, leading to a decrease in performance and potential damage. In this article, we will discuss the essential role of compression, symptoms of compression loss, and what can cause a cylinder to lose compression.
Essential Role Of Compression
Compression is a crucial component of the engine’s combustion process. It creates pressure that allows the air and fuel mixture to ignite, powering the engine. Without compression, the engine would not function. Proper compression ensures that the engine runs efficiently and smoothly, providing maximum power and performance. If there is a loss of compression, the engine will not run correctly, leading to potential damage and decreased performance.
Symptoms Of Compression Loss
Compression loss can cause several symptoms that indicate an issue with the engine. These symptoms include:
- Decreased power and performance
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Engine misfires
- Excessive oil consumption
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Engine knocking or tapping sounds
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to have your engine checked by a professional mechanic to diagnose the issue.
What Can Cause A Cylinder To Lose Compression
Several factors can cause a cylinder to lose compression, including:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Worn Piston Rings | Piston rings can wear down over time, leading to a loss of compression. |
| Valve Problems | Issues with the valves, such as a broken valve spring or bent valve, can cause compression loss. |
| Blown Head Gasket | A blown head gasket can cause compression loss between cylinders. |
| Cracked Cylinder Wall | A cracked cylinder wall can allow air to escape, leading to a loss of compression. |
In conclusion, compression plays an essential role in the engine’s combustion process. A loss of compression can cause several symptoms, including decreased power and performance, difficulty starting the engine, and engine misfires.
Several factors can cause a cylinder to lose compression, including worn piston rings, valve problems, a blown head gasket, and a cracked cylinder wall. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to have your engine checked by a professional mechanic to diagnose the issue.
Failed Head Gasket
A failed head gasket is a common cause of compression loss in a cylinder. This vital component sits between the engine block and cylinder head, sealing the combustion chamber and maintaining proper pressure levels.
Signs Of A Blown Head Gasket
- Overheating engine
- White exhaust smoke
- Milky oil
- Loss of coolant
- Visible external leaks
Impact On Cylinder Compression
When a head gasket fails, it can lead to a loss of compression in the affected cylinder. This occurs as the gasket no longer effectively seals the combustion chamber, allowing compression to escape. As a result, the cylinder may experience reduced power and efficiency, leading to engine misfires and decreased performance.
Worn Piston Rings
Worn piston rings can be a significant factor in causing a cylinder to lose compression. The piston rings play a crucial role in maintaining proper compression within the cylinder. When these rings wear out, it can lead to a range of consequences that affect the engine’s performance.
Role Of Piston Rings
Piston rings are vital components that seal the combustion chamber, preventing the fuel and air mixture from leaking into the crankcase. They also help to regulate oil consumption by scraping excess oil off the cylinder walls. Additionally, piston rings aid in transferring heat from the piston to the cylinder wall. These functions are essential for maintaining optimal compression within the cylinder.
Wear And Tear Consequences
As piston rings wear out, they become less effective in sealing the combustion chamber, resulting in reduced compression. This can lead to loss of power, increased oil consumption, and poor engine performance. Moreover, worn piston rings can allow oil to enter the combustion chamber, leading to excessive smoke emission and potential damage to the catalytic converter.
Valve Train Issues
The valve train is a critical component of the engine that plays a vital role in maintaining proper compression in the cylinders. When there are issues with the valve train, it can lead to a loss of compression, resulting in poor engine performance. Two common valve train issues that can cause cylinder compression loss are valve damage and leakage.
Valve Damage
Valve damage can occur due to several factors, such as excessive wear, improper seating, or impact from foreign objects. When the valves are damaged, they may not close properly, leading to a loss of compression. This can happen if the valve faces become worn or pitted, preventing them from creating a tight seal with the valve seats.
In some cases, the valves may also become bent or warped, causing them to not seat correctly and allowing compression to escape. This can happen due to overheating, high engine speeds, or a timing belt failure. If the valves are damaged, they need to be inspected and replaced if necessary to restore proper compression.
Leakage
Another common issue with the valve train that can cause compression loss is leakage. This can occur when there are leaks in the valve seals, valve guides, or valve stem seals. These seals are responsible for preventing oil from entering the combustion chamber and also for keeping the compression gases from escaping.
When the seals are worn or damaged, oil can seep into the combustion chamber, leading to decreased compression. Additionally, if the valve guides are worn, they may allow excessive movement of the valves, causing compression loss. It is important to regularly inspect and replace these seals and guides to prevent leakage and maintain optimal compression.
Effects On Engine Performance
A loss of compression due to valve train issues can have significant effects on engine performance. When compression is compromised, the engine may experience a decrease in power, reduced fuel efficiency, and rough idling. The cylinder affected by the compression loss may also exhibit misfires, causing a noticeable decrease in overall engine performance.
Furthermore, if the compression loss is severe, it can lead to engine stalling or difficulty starting the vehicle. Ignoring valve train issues can result in further damage to the engine and potentially expensive repairs. Therefore, it is crucial to address any valve train issues promptly to maintain optimal engine performance.
Cylinder Wall Damage
Cylinder wall damage can lead to loss of compression in an engine. Causes include worn piston rings, scored cylinder walls, or a blown head gasket. These issues can result in reduced engine performance and should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage.
Causes Of Cylinder Scoring
There are several factors that can lead to cylinder wall damage, commonly known as cylinder scoring. This type of damage can cause a loss of compression in the cylinder, leading to decreased engine performance. Understanding the causes of cylinder scoring is crucial for diagnosing and addressing the issue effectively.
One of the main causes of cylinder scoring is inadequate lubrication. When the oil supply to the cylinder walls is insufficient, the friction between the piston rings and the cylinder wall increases. This increased friction can result in the metal surfaces rubbing against each other, leading to scoring and damage.
In addition to inadequate lubrication, another common cause of cylinder scoring is the presence of foreign particles or contaminants. These particles can enter the combustion chamber through various means, such as worn piston rings or damaged seals. Once inside, they can scratch the cylinder walls, causing scoring and reducing compression.
Furthermore, improper engine cooling can also contribute to cylinder scoring. When an engine runs too hot, the excessive heat can cause the cylinder walls to expand, leading to increased friction and potential scoring. Similarly, inadequate cooling can result in insufficient heat dissipation, causing the cylinder walls to overheat and become susceptible to damage.
Detecting Wall Imperfections
Identifying wall imperfections in the cylinder is crucial for diagnosing the cause of compression loss accurately. There are several signs to look out for that can indicate cylinder wall damage.
One common indicator of wall imperfections is a noticeable decrease in engine power and performance. If you notice that your vehicle is struggling to accelerate or experiencing a loss of power, it may be a sign of cylinder scoring and compression loss.
Another way to detect wall imperfections is through a compression test. By measuring the compression pressure within each cylinder, you can identify any significant variations that may point to a damaged cylinder wall. Additionally, a leak-down test can help pinpoint the exact location and extent of the compression loss.
Visual inspection is also a valuable method for detecting wall imperfections. By removing the cylinder head and inspecting the walls for scratches, gouges, or signs of excessive wear, you can determine if cylinder scoring is the cause of the compression loss.
Overall, understanding the causes of cylinder scoring and knowing how to detect wall imperfections are essential for addressing compression loss effectively. By identifying and resolving the underlying issues, you can restore the optimal performance of your engine and prevent further damage.
Timing Belt Or Chain Problems
When it comes to engine compression loss, timing belt or chain problems can be a significant factor. Issues with the timing belt or chain can lead to timing disruption, ultimately causing a decrease in cylinder compression.
Timing Disruption Effects
Improper Timing: A worn or stretched timing belt or a broken timing chain can disrupt the synchronization between the camshaft and crankshaft, leading to improper valve timing and reduced compression.
Valve Damage: In cases of severe timing belt or chain failure, the valves may come into contact with the pistons, causing damage to both components and resulting in compression loss.
Complete Engine Failure: If the timing belt or chain snaps while the engine is running, it can lead to catastrophic engine failure and extensive damage to internal components.
Preventative Maintenance Tips
Regular Inspections: Ensure that the timing belt or chain is inspected and replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals to prevent premature wear and potential failure.
Addressing Noise: Any unusual noise coming from the timing cover area should be promptly investigated as it may indicate issues with the timing belt or chain.
Professional Replacement: When replacing the timing belt or chain, it is crucial to have the procedure performed by a qualified mechanic to ensure proper installation and timing synchronization.
Carbon Deposits
Build-up Of Carbon
Excessive carbon deposits can lead to compression loss in cylinders.
Cleaning Techniques
To remove carbon build-up, use techniques like:
- Manual scraping
- Chemical cleaners
- Media blasting
Diagnosing Compression Issues
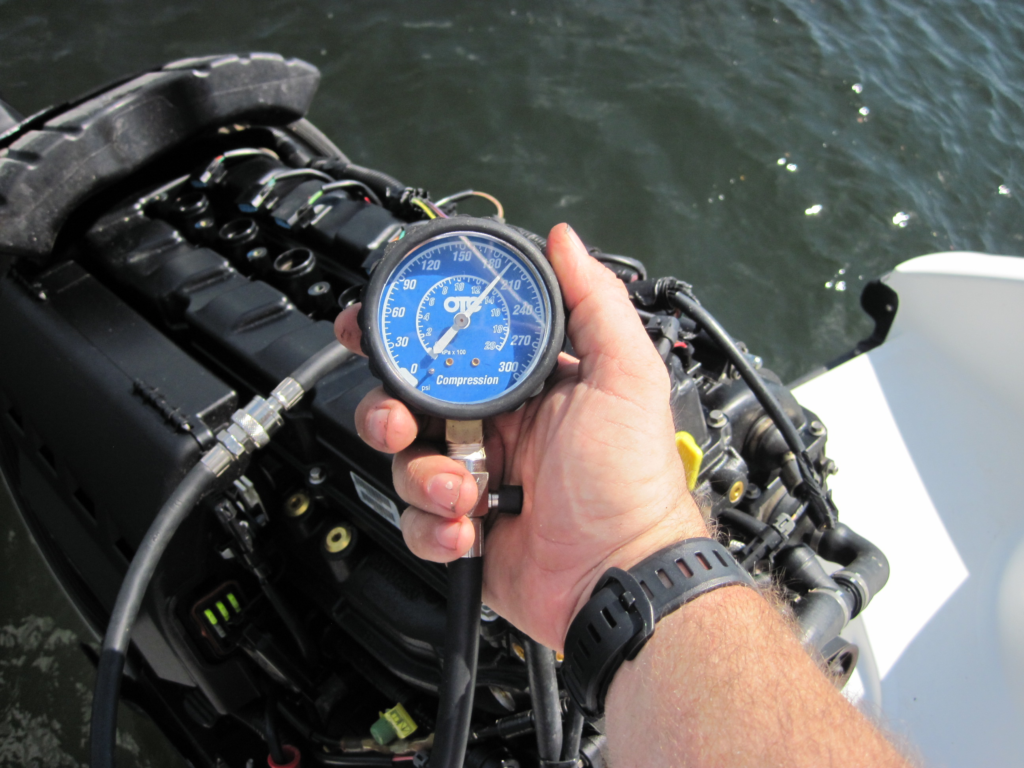
Compression issues in a cylinder can be caused by various factors. To accurately diagnose these problems, using a compression tester is crucial.
Using A Compression Tester
1. Remove all spark plugs and disable the ignition system.
2. Attach the compression tester to the spark plug hole of the cylinder.
3. Crank the engine several times to get a reading on the gauge.
Interpreting Test Results
1. Healthy Cylinder: Compression readings should be consistent across all cylinders.
2. Low Compression: Indicates issues like worn piston rings or a damaged cylinder head gasket.
3. No Compression: Points to severe problems like a cracked cylinder head or valve issues.
Repair And Prevention Strategies
Cylinder compression loss can be caused by various factors such as worn piston rings, damaged valves, or a blown head gasket. It is important to address these issues promptly with repair and prevention strategies to maintain the efficiency and performance of the engine.
Common Repair Solutions
In case of low compression, inspect and replace damaged piston rings.
Long-term Engine Care
Regularly change oil to prevent carbon buildup on valves.
Inspect and replace worn-out valves and valve seats.
Ensure proper installation of head gasket to prevent leaks.
Use high-quality fuel to prevent carbon deposits in cylinders.
Implement timely maintenance to prevent compression loss.
Common Repair Solutions
– Inspect and replace damaged piston rings.
– Check and repair any cracks in the cylinder walls.
– Address any issues with the cylinder head gasket.
– Test and replace faulty valves or valve seats.
Long-term Engine Care
1. Regularly change oil to prevent carbon buildup.
2. Monitor and maintain proper fuel-air mixture.
3. Utilize quality fuel to reduce carbon deposits.
4. Implement regular engine inspections and maintenance.
Conclusion
To sum up, a cylinder may lose compression due to various reasons such as worn piston rings, damaged valves, or a blown head gasket. It is essential to diagnose the root cause of the issue and fix it promptly to avoid further damage to the engine.
Regular maintenance and timely repairs can help prevent compression loss and increase the lifespan of your vehicle. So, if you notice any signs of compression loss, it’s best to get it checked by a professional mechanic.
Our mission is to be your trusted resource for everything related to car cylinders.